🚀 Introduction
The arrival of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT was a watershed moment for artificial intelligence. We were collectively fascinated by their ability to generate human-like text, write code, and create art from simple prompts. They became our indispensable creative assistants, drafting emails, brainstorming ideas, and summarizing vast amounts of information.
However, as the initial awe settled, a new realization emerged: while LLMs are incredibly powerful cognitive engines, they are often “one-man shows” – limited by their inability to independently plan, execute multi-step tasks, and interact dynamically with the world.
This realization has sparked a massive shift towards Multi-Agent Systems (MAS). These are not just single AI models but teams of specialized, autonomous agents that collaborate to achieve complex goals. If an LLM is a brilliant individual contributor, a Multi-Agent System is a high-performing, cross-functional team.
🔄 The Evolution of AI and the Business Case for Agents
📈 The Evolutionary Leap
The journey of AI has been a progression from rigid, rule-based systems to the flexible, probabilistic world of deep learning and LLMs. The next evolutionary leap is from these passive models to active, goal-driven agents.
An AI agent (definition keeps changing over time) is a system that can:
- 👁️ Perceive its environment
- 🧠 Reason about it
- 📋 Plan a sequence of actions to achieve a goal
- ⚡ Execute those actions using tools
A Multi-Agent System takes this a step further. It involves multiple such agents, each with a specific role and expertise, working together. For example:
- 🔬 One agent might be a “Researcher”
- 💻 Another a “Coder”
- 🧪 A third a “Tester”
They communicate, share information, and coordinate their actions to solve problems that are too complex for any single agent to handle alone. This mimics human organizational structures, where complex projects are broken down and assigned to specialists.
📊 AI Development Evolution
| Phase | Focus | Capability |
|---|---|---|
| ⚙️ Rule-Based Systems | Deterministic logic | Limited automation |
| 🤖 Machine Learning | Pattern recognition | Predictive insights |
| 🧠 Deep Learning | Representation learning | Perception & NLP |
| 💬 Large Language Models | Generalized reasoning | Natural language cognition |
| 🤝 Multi-Agent Systems | Distributed cognition | Autonomous orchestration |
📊 The Data Behind the Shift
This isn’t just a theoretical shift; it’s backed by significant market momentum and investment.
💰 Market Growth Indicators
Key Enterprise Trends:
- 💼 The global AI market is projected to exceed $1.5 trillion by 2030, driven by enterprise automation
- 💵 Enterprise AI budgets are shifting from experimentation to operational AI systems
- 🏢 Venture funding for agentic AI frameworks has grown rapidly, with startups focusing on autonomous systems and workflow orchestration
- 📊 Enterprises report that productivity copilots improve efficiency by 15–30%, but agent-based automation can drive cost reductions exceeding 40% in certain workflows
💵 The Imperative of “Hard” ROI
For businesses, the move to MAS is driven by the need for “hard” return on investment (ROI). While LLMs can improve individual productivity, MAS can automate entire business processes, leading to measurable financial outcomes.
From Efficiency to Direct Savings
- ✅ Verifying the user's identity
- ✅ Checking the order status in a database
- ✅ Processing the payment reversal
- ✅ Sending a confirmation email
Driving Revenue and Reducing Waste
In supply chain management, companies using advanced multi-agent systems have reported an average 15% reduction in overall supply chain costs. A MAS can:
- 🔮 Predict disruptions
- 📦 Optimize inventory levels in real-time
- 🚚 Autonomously reroute shipments
- ❌ Prevent costly stockouts and reduce waste
This translates directly to the bottom line.
🏭 Practical Examples of Multi-Agent Systems
Here are real-world examples where Multi-Agent Systems are moving beyond fascination to deliver tangible functionality:
1. 📦 Supply Chain & Logistics Optimization
A global retailer can employ a MAS where different agents represent suppliers, warehouses, and logistics providers:
🔍 Sensing Agent → Detects port strike in news
↓
🧠 Planning Agent → Assesses impact with Inventory Agents
↓
📊 Inventory Agents → Check stock levels at warehouses
↓
🚚 Logistics Agents → Autonomously re-route shipments
↓
✅ Crisis Averted → Before manager opens emailImpact: Prevention of major supply chain disruption through autonomous decision-making.
2. 💹 Advanced Financial Analysis & Risk Management
A hedge fund can use a MAS to analyze investment opportunities:
| Agent Type | Specialization | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 📰 News Analyst | Sentiment Analysis | Parse real-time financial news and social media |
| 📊 Quantitative Analyst | Statistical Modeling | Run complex models on historical market data |
| ⚠️ Risk Assessment | Downside Analysis | Evaluate potential risks and downsides |
| 🎯 Aggregator | Synthesis | Consolidate findings into comprehensive recommendation |
Impact: Multi-faceted investment recommendations that no single model could generate.
3. 💻 Software Development and Evaluation
A tech company can use a MAS to automate its code review process:
Impact: Accelerated development cycle with improved software quality.
🏗️ Multi-Agent System Architecture
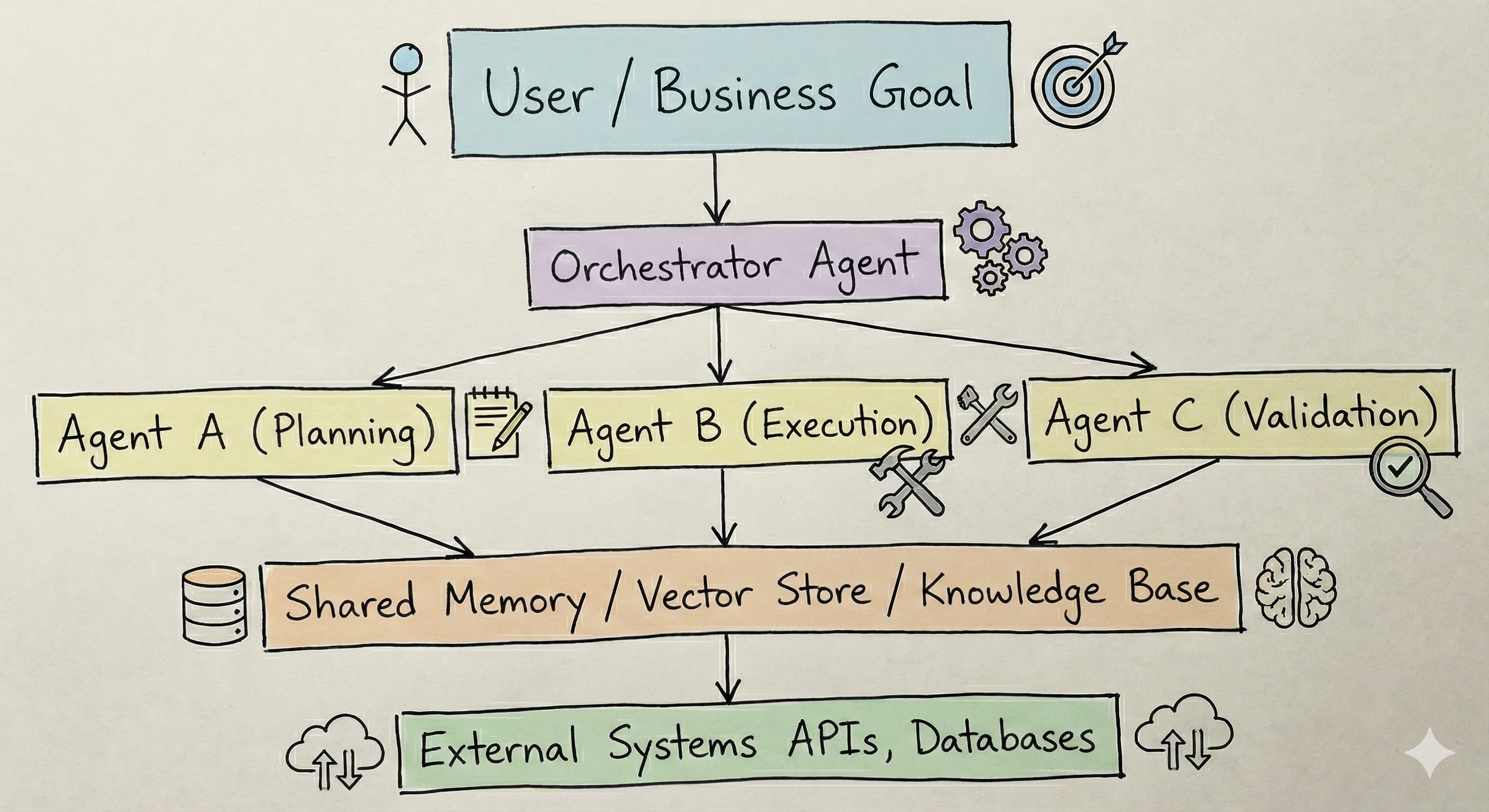
To understand how these systems work, let’s examine their architecture and implementation.
🔀 Architectural Paradigm Shift
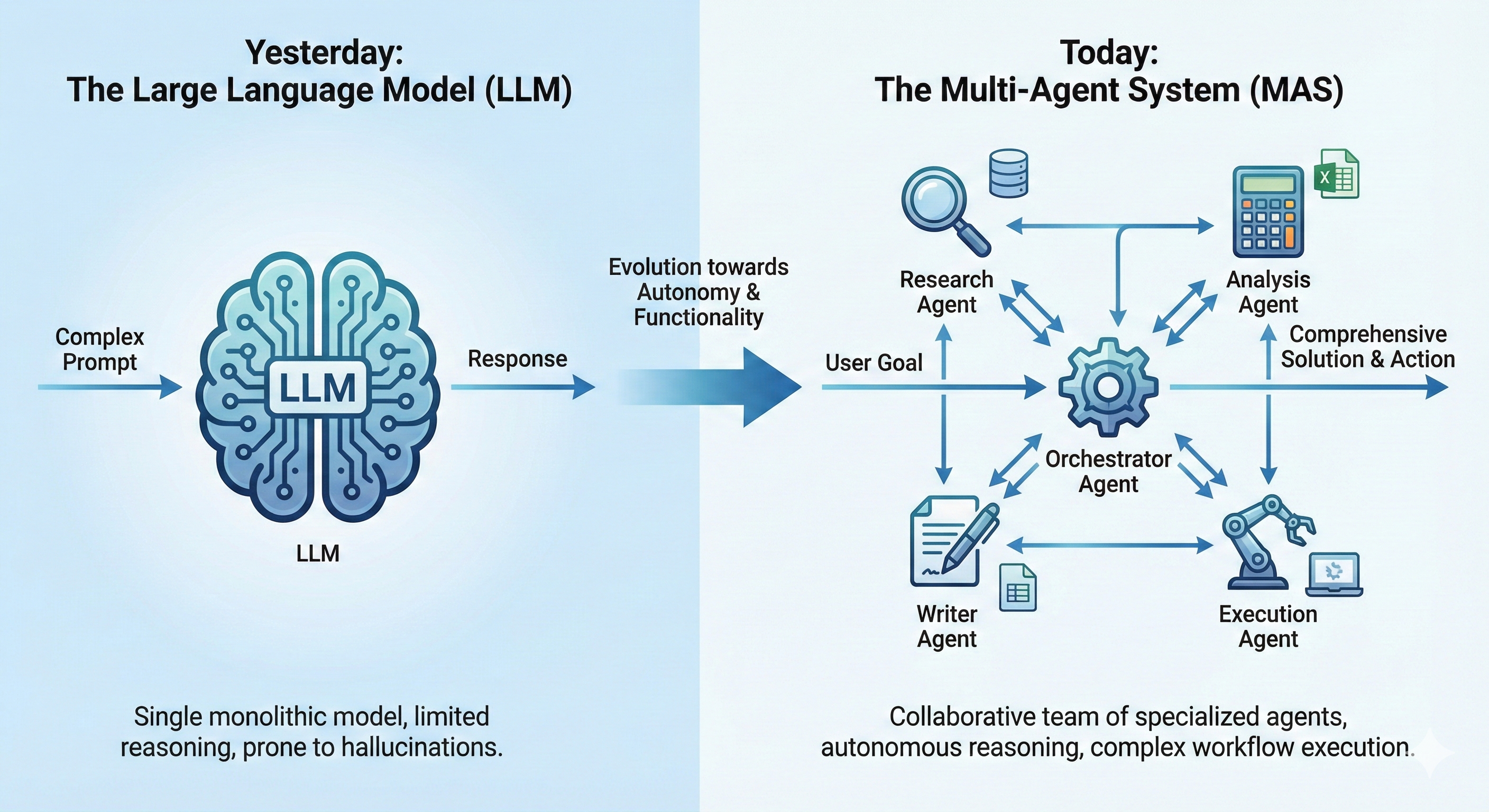
🏛️ High-Level Architecture
💻 Simple Conceptual Code Example
This conceptual Python code, using a fictional agency framework, illustrates how you might define a simple MAS with a researcher and a writer:
# Conceptual example of a Multi-Agent System using a hypothetical framework
from agency import Agent, Task, Team
# 1. Define your specialized agents with distinct roles and goals.
# The 'Researcher' agent is given a tool to search the web.
researcher = Agent(
role='Senior Researcher',
goal='Uncover cutting-edge developments in AI and summarize them.',
backstory="You are an expert at finding and synthesizing complex information from the web.",
tools=['web_search_tool'], # Hypothetical tool
verbose=True
)
# The 'Writer' agent takes information and crafts it into a blog post.
writer = Agent(
role='Tech Blog Writer',
goal='Write compelling and accessible blog posts about tech trends.',
backstory="You are a skilled storyteller who can explain complex technical concepts to a broad audience.",
verbose=True
)
# 2. Define the tasks that need to be completed.
# Task 1 is for the researcher to find information on a specific topic.
task1 = Task(
description='Conduct comprehensive research on the latest advancements in Multi-Agent Systems (MAS). Focus on real-world applications.',
agent=researcher
)
# Task 2 is for the writer to create a blog post based on the research from Task 1.
task2 = Task(
description='Using the research provided, write a 500-word blog post about the future of MAS. The tone should be professional and optimistic.',
agent=writer,
context=[task1] # This task depends on the output of task1
)
# 3. Create a team and assemble the agents and tasks.
# The Team orchestrates the workflow, ensuring tasks are completed in the correct order.
ai_content_team = Team(
agents=[researcher, writer],
tasks=[task1, task2],
verbose=True
)
# 4. Kick off the process.
result = ai_content_team.kickoff()
print("Final Blog Post Output:")
print(result)🎯 Conclusion
The transition from single Large Language Models to Multi-Agent Systems marks a critical inflection point in the development of AI. We are moving beyond the initial fascination with AI’s creative potential and into a new phase focused on practical, autonomous functionality.
🔑 Key Takeaways
Those who embrace this shift, moving from piloting simple chatbots to orchestrating sophisticated multi-agent systems, will be the ones to unlock the true, transformative value of AI and achieve significant, measurable return on investment.
👋 Join the Conversation
What are your thoughts on Multi-Agent Systems? Have you experimented with agentic AI in your organization? Share your experiences and questions in the comments below!
Next in the series: Deep dive into orchestration patterns and frameworks for building production-ready Multi-Agent Systems.